Light is a form of energy plants readily utilize to carry out photosynthesis. Most terrestrial plants would not be able to grow and produce food without light to induce the processes essential to support life. Oxygen is the byproduct of photosynthesis which supports all other forms of life on the planet. Therefore, it is a worthwhile endeavor to ensure that our plants grow healthy whether we grow them outdoors or indoors. When growing plants indoors, artificial light will work almost as well as sunlight, given that they contain the wavelengths needed with certain intensities. Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) are efficient bulbs used to customize or emulate the natural light spectrum.
Not all LEDs ensure efficient and healthy plant growth. Regular LED lights might not contain the desired light spectrum for optimal plant development. Therefore, LED grow lights are configured in a panel with the most ideal set of wavelengths for growing plants indoors. LED grow lights are cost-effective, energy efficient and have ultra-low heat output, making them the most viable light source for growing plants indoors. LED grow lights are available in monochromatic pure colors (that is, they contain only one wavelength or a very small range of wavelengths that they appear a certain color to the naked eye) and can be tailored to make a spectrum conducive for plant growth. A panel with LEDs of different wavelengths is typically employed so that the plants are exposed to multiple wavelengths with varying intensities at a time. Because of this, LEDs are useful for all growth stages.
Plants have pigments that allow them to absorb light for photosynthesis. Each pigment has absorbance that varies with different wavelengths, so the best wavelengths for a certain plant depend on the abundance of the pigments it contains. Chlorophyll A appears to be green as it reflects green light and is the most abundant pigment in most plants. It absorbs blue and red light. Chlorophyll B (similar to Chlorophyll A) also absorbs blue and red light but with a less extensive wavelength range. Plants abundant in Carotenoids appear to be red, orange or yellow as the pigment reflects the longer light wavelengths. Carotenoids absorb blue-green light. The image below shows the relative absorption of light (300 nm-700 nm) by photosynthetic pigments.
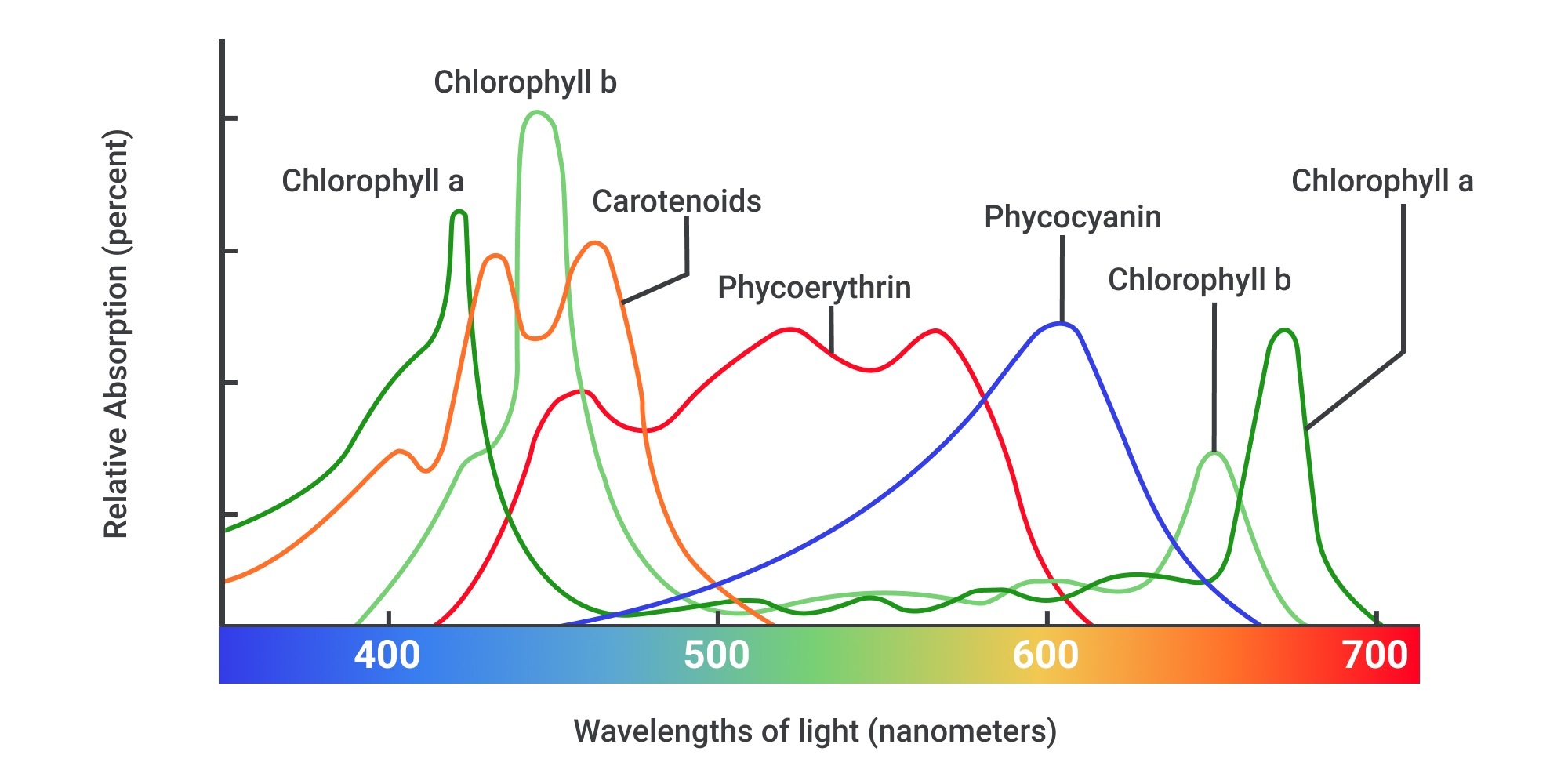
From the absorption spectrum, it can be seen that the two essential colors in LED lamp panels that grow plants are blue and red. Blue light plays a big role in the plant’s initial growth stage as it stimulates stomatal opening and stem elongation while red light encourages flowering and budding. Adding green to the light spectrum can enhance leaf expansion rate and increase the biomass yield. Blue and red LEDs are the cheapest to produce and are the most commonly used in combination, hence light from LED panels used to grow plants appear to be purple. As blue is essential to the early development of plants and most pigments readily absorb blue wavelengths, LEDs with higher blue intensities are preferred over LEDs with more red.
Diode grow lights should provide the right light spectrum for photosynthesis, which is key to plant development. Before purchasing, make sure to check the provided spectrum of the grow lights and the needs of the type of plant you are planning to grow. Other considerations in growing plants indoors include the growing area, light placement, and daily length of exposure of the plants to the LEDs.